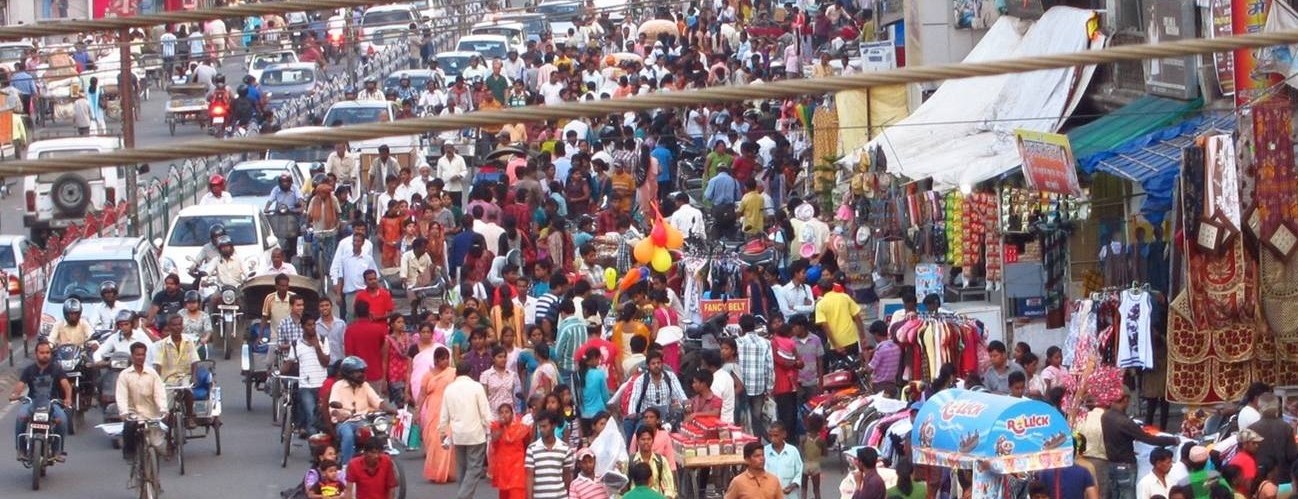
In the next fifteen years, the top hundred cities of India will grow by around 60 percent. These cities will have 125 million new inhabitants, roughly the population of Japan! Today, with less than a third of all urban trips on personal motor vehicles (and less than 10% by personal cars), and more than two thirds by sustainable modes—walking, cycling, and public transport—Indian cities look good on paper. But, the ground reality is different.
Formal public transport is poor or non-existent. Uncomfortable, unsafe, and polluting paratransit services fill the gap in most cities. Walking and cycling facilities are completely missing, or unusable if they exist. People use ‘sustainable’ modes out of financial compulsion, not out of choice. Cities are choked with traffic and pollution. Road fatality rates are 20-25 times that of developed countries.
On the other hand, personal motor vehicle ownership is doubling every decade, at nearly thrice the rate of population growth. As more and more people depend on personal motor vehicles for their daily travel needs, cities try to accommodate this deluge of traffic by expanding roads, building flyovers, and increasing parking space. However, such automobile centric planning practices cause urban sprawl, resulting in longer commutes and more traffic on the roads. Infrastructure costs, user costs, travel times, and pollution increase; traffic safety worsens.
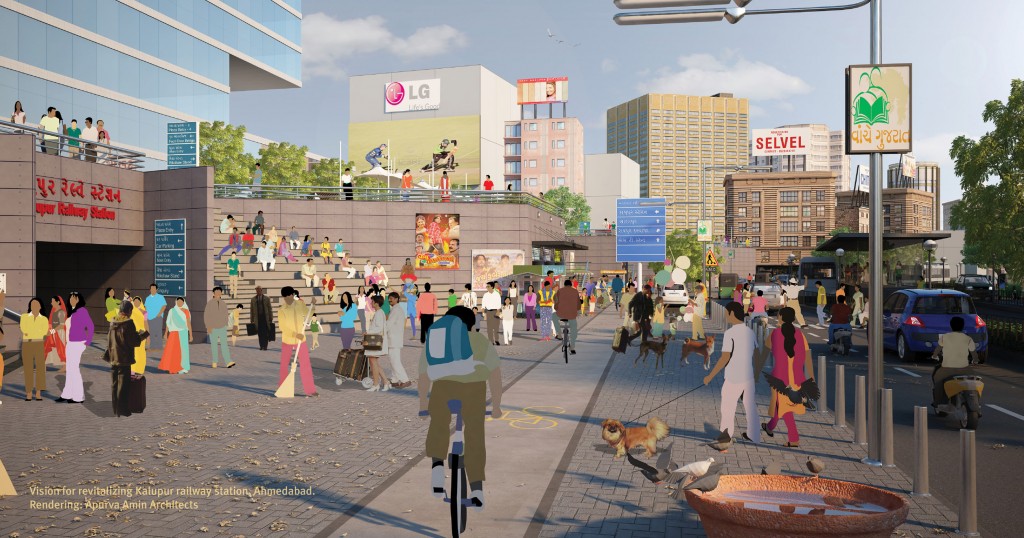
To become smart, Indian cities must embrace a radically different approach to urban mobility: one that focuses on efficient and sustainable forms of mobility like public transport, walking and cycling. They also need to adopt a transit-oriented development (TOD) approach to create dense yet livable neighborhoods along mass transport lines, so that trips remain short and convenient and cities remain compact.

Large and medium-sized Indian cities must invest in an extensive network of rapid transit along with a wide coverage of frequent, high-quality urban bus service. Further, cities of all sizes must invest in safe and convenient walking and cycling infrastructure. The aim should be to provide safe, convenient, and attractive mobility options for all while restricting the vehicle-kilometres travelled (VKT) by personal motor vehicles to no more than present levels. In mode share terms, percentage of trips by personal motor vehicles should be cut by half of present level by 2031.
Rapid transit in India: A global comparison
A global comparison of rapid transit projects reveals that India has just 3.2 kilometers of rapid transit per million urban residents (counting only cities with population of more than half million), a third of its peers China and Brazil, and less than a twentieth of France. To keep pace with its urban growth, India needs over a eight-fold increase of its mass rapid transit supply by 2031. However, at the present rate of building rapid transit in India, it would take at least 3-4 times longer, by when, the need for rapid transit would increase even further. India is not investing in sustainable urban transport at anything close enough to meet even basic mobility needs, much less to addressing the issues of inequity and environmental degradation that are growing faster than the population.
Countries like Brazil, Colombia, and Mexico not only have much more urban rapid transit per capita than India but are expanding their systems at significantly faster rate. The reason behind this is bus rapid transit (BRT)—an inexpensive and quick to implement rapid transit mode that can provide metro-quality service with the added benefit of flexibility of rubber-tyred buses compared to rail systems. BRT systems not only have dedicated median lanes to bypass congestion but also have feature elements like stepless boarding, off-board fare collection, and real-time passenger information that reduce delays and improve customer service.
BRT and bus-based public transport in India
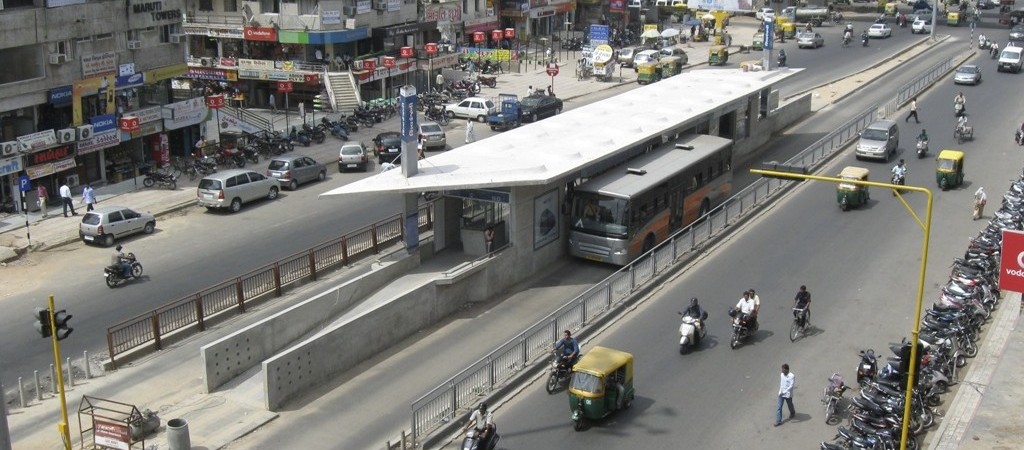
The Ahmedabad BRT system—known as Janmarg or “the People’s Way”—has revolutionised expectations about bus-based mass rapid transit in India. In a span of five years from 2009 to 2014, Janmarg has expanded from a 12.5 km corridor to a network of 88 km, providing connectivity across the city. Janmarg demonstrates that BRT can provide high-quality service at a fraction of the cost and has inspired similar BRT efforts like Rajmarg (Rajkot) in 2012, iBus (Indore) in 2013 and Citilink (Surat) in 2014.

Features of Bus Rapid Transit
In 2015, Pune-Pimpri Chinchwad inaugurated Rainbow BRT. Bus operations are monitored from a central control centre using real-time data from GPS tracking devices on buses. The system uses a fleet of Euro IV CNG buses to contain emissions. With a daily ridership of 130,000, Rainbow BRT has helped reduce reliance on personal motorized vehicles. Around 12 percent of Rainbow BRT commuters used personal motor vehicles for their daily travel earlier.
Rapid transit, while important, is not enough. Many Indian cities have skeletal bus services or none at all. In their absence, people depend on intermediate public transport modes that are unsafe and, often, highly polluting. Hence, a formal bus-based public transport service is a necessity in all cities. In all, Indian cities will need over 3 lakh new city buses and minibuses in operations by 2031.
Walking and cycling: Basics of urban transport
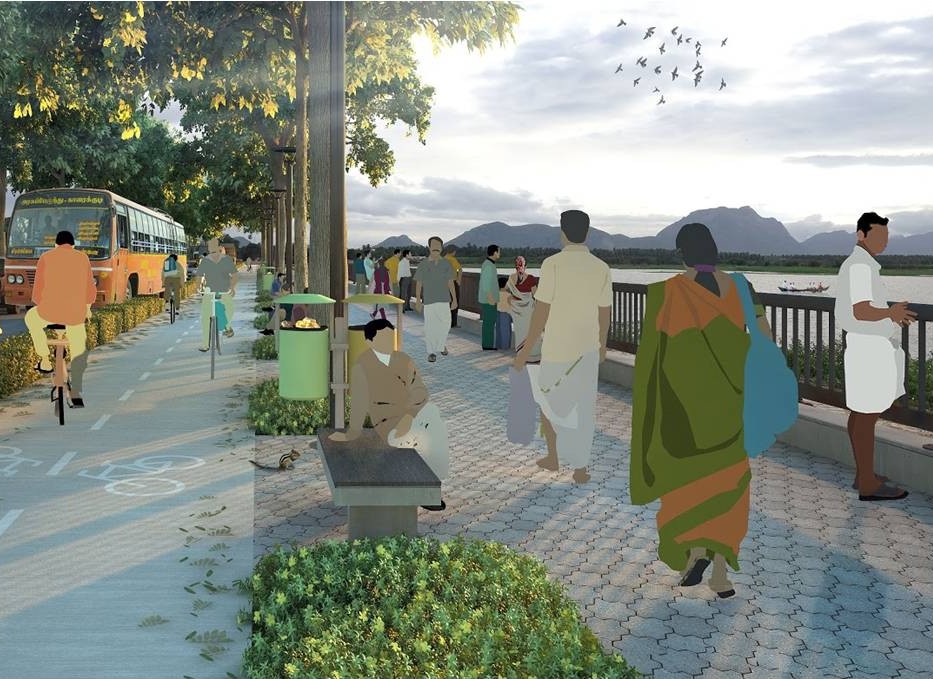
More than a third of all the trips in our cities are made by foot or cycle. Public transport trips too start and end on foot—making walking integral to India’s transport systems. Cities must focus on redesigning streets to support walking and cycling—clean modes of transport that still play an important role in Indian cities. Indian cities need to build at least 32,000 km of wide and accessible footpaths and 16,000 km of safe and convenient cycle tracks over the next fifteen years.
Chennai is the first Indian city to adopt a non-motorised transport policy to promote walking and cycling in the city. The Corporation of Chennai has proposed to create a safe and pleasant network of footpaths, cycle tracks and greenways through the entire city to arrest the current decline in walking and cycling. 26 streets have been redesigned with better walking infrastructure, with another 20 streets under construction. Streets with wide carriageways and narrow or no footpaths have been replaced by wide, continuous and unhindered walking spaces, safe pedestrian crossings, properly scaled carriageways, conveniently placed bus stops, and clearly designated on-street parking.
Building cities around transit
Investments promoting walking, cycling and public transport will not bear fruit unless Indian cities stop counterproductive car-centric investments like flyovers and elevated roads. No city in the world has solved its congestion problem by building more roads. Our cities should follow a simple mantra: Build transit, Add density, Control parking. Cities should encourage higher densities in areas where there is good connectivity to mass rapid transit. They must also actively control personal motor vehicle use through parking restrictions and market-based pricing. Parking fees should be pegged to parking demand—higher demand, higher fee. Revenue generated from parking can be used to build better walking and cycling infrastructure and to expand public transport.
Ahmedabad’s Development Plan 2021 embraces this mantra. It encourages the use of public transport and promotes a compact city by encouraging higher density commercial and residential activities along BRT and Metro corridors while removing minimum requirements for off-street parking in new buildings. In fact, there is a cap on the amount of parking that new buildings can create—a maximum of two basement levels. Any additional parking will be deducted from the permitted FSI.
Pune Municipal Corporation (PMC), through its draft parking policy, makes a case for limited parking. In areas with good connectivity to mass rapid transit, the emphasis is on controlling parking supply. As per the policy, the city will be divided into multiple parking districts. Parking rates in these districts will reflect rentals in the area, the size of the vehicle and the levels of congestion in the area.

PMC has also proposed in its 2016-17 budget to spend 50% of its transportation budget on footpaths, cycle tracks, and BRT, thus prioritising spending on sustainable transport over car-oriented infrastructure. Revenue generated from parking will also be used to build streets with better walking and cycling infrastructure as well as to expand public transport. Many vehicle-free zones are also planned, particularly on busy shopping streets.
The way forward
Benefits of adopting such a sustainable transport approach are many. It can bring down capital expenditure, fuel consumption, pollution levels and travel costs, saving money for government and individual citizens. Building safe streets that support the needs of all road users can also save tens of thousands of lives.
The Smart Cities Challenge has clear guidelines to promote walking, cycling, and public transport and will see an investment of around one trillion rupees (including central, state, and city contributions) over the next five years to develop best practices in the urban sector. Though these are good signs, implementation challenges remain. Access to funds, while essential, is not enough. Cities must also improve their capacity to plan and deliver high quality projects, by creating institutions with clear authority to plan, design, and implement. Smart are those cities that have the ability to create a sustainable, equitable and livable future.
The article was first published in Urbana World, Mar-Apr 2016