Standing at a crucial intersection, bus transportation faces the possibility of being a footnote in Indian history. Lest we forget, buses were, and in most cases continue to be, the backbone of a city’s travel needs. But at the turn of the century, globalisation established its roots in Indian cities and with it arrived new technology, improved purchasing power, and far-reaching aspirations—fuelled by marketing gimmicks.
Soon enough, the idea of the first car parked itself deep into the psyche of the masses. Interestingly, the messaging was altered according to socio-economic backgrounds. From the first motorcycle to the first scooter (eventually rebranded as the ‘scooty’). Well, why should cars have all the fun!
Etched in our memories by means of rampant baits (adverts of all sizes and forms), automobiles were perpetuated as the vehicles for our ‘escape from Alcatraz’. Just for one tiny-little gargantuan problem! The light that flickered at the end of that tunnel was decimated by tonnes of reinforced steel and million gallons of cement. That is, the more infrastructure we built to support private motor vehicles the more congestion was created on the streets; resulting in ever-increasing pollution levels.
As per a report, published by the University of Chicago, automobiles contribute a quarter of the PM 2.5 released into the atmosphere. “Particulate pollution cuts global life expectancy short by nearly two years; and in India, it is an average of four years! In comparison, smoking cuts global life expectancy by 1.6 years,” states the report.
And in all of this, commute hours only managed to worsen. Hence, countries at large are adopting sustainable and ecological public transport measures such as buses. But in India, there still exists a certain disdain when it comes to using buses in the urban scenario.
In order to rid ourselves of this baseless confirmation bias, we need to understand what these myths are and where they stand when viewed with rationale.

The comfort of a private vehicle comes with a certain privilege and in time, anything outside of that zone is viewed with a myopic lens. A huge part of this delusion is that everyone travels by either car, two-wheelers, or now, cabs. The fact, though, is different from the distortion.
Less than a fourth of all trips are on personal motor vehicles and cabs, while over a quarter is made on public transport. And, city buses cater to most of the public transport trips in major Indian cities. Like in the case of Bengaluru and Delhi, where bus services record more than five million trips per day. This begs the question, where are the buses?!
In the case of Chennai, with a population touching close to 10 million, there are just about 4,000 operational buses in the city. According to national service level benchmarks, there should be 400 – 600 buses per million inhabitants in cities. Most Indian cities fall short of this number. Going by that standard, Chennai records a shortfall of close to 2,000 buses. Even so, the city’s Metropolitan Transport Corporation (MTC) records an incredible 4.7 million daily ridership—resulting in overcrowding and poor level of service.
To cope up with the demand and maintain a decent level of service, cities need to be assisted either by state or national schemes. Though the JNNURM scheme drew sharp criticism, it helped bring about a massive influx of high-quality fleet—more than 13,000 buses were added to city bus systems across the country.
Indian cities aren’t the exception to the public transportation thumb rule. Cities across the world, both developed and developing, register higher bus ridership figures than any other public transport system. These include London, Singapore, Hong Kong, Mexico City, São Paulo, etc.

Let’s begin by addressing the elephant in the room. Buses, though big, are not the reason behind congestion on roads. The credit goes to private motor vehicles, like cars and two-wheelers, which through their sheer numbers manage to clutter every possible infrastructure created to ease their passage.
Back in 1991, Munster, in Germany, put on display a three-panelled photograph. Titled ‘Waste of Space’, it depicted the space required to transport 72 people by either car, bus or bicycle. And as the adage goes: an image is worth a thousand words. To spell it out, cars occupy a lot more space and carry a lot lesser people. Whereas, a bus can carry a lot more people and occupy a lot less space on the road.
Here are some stats to bolster this argument: a bus, while thrice the size of a car it carries thirty times more passengers during the course of a day in a typical Indian city. While cars occupy most of our street space, they serve less than a fourth of all trips. They also sit idle for 95 per cent of the time. And just like an elephant cannot survive on peanuts, infrastructure (flyovers, free parking lots, road expansion, etc.,) to support private automobiles burns meteor-sized holes in public expenditure.

Now, cynics would argue that realistically buses get stuck for longer in traffic and comfort levels vary according to passenger density or crowding. Well, obviously! If you pack roads, of how-many-ever lanes, with a swarm of private motor vehicles no one would be able to commute efficiently. But what if buses have a lane of their own?
In the present scenario, a city spends around Rs 200-300 crore per km in building a four-lane flyover to increase capacity by 60%. Whereas, investing in a bus-rapid transit (BRT) at-grade would ensure road capacity to increase anywhere from 400-1,000 per cent and cost approximately Rs 20 crore per km—just one-tenth the cost of building a flyover. When designed at par with international standards, the BRT system not only transports more commuters but ensures faster transit and accessibility to folks from all walks—especially the differently-abled and children.
Hence if cities are looking for efficient modes of transport, a rapid transit system such as the BRT is the answer.

There is no doubt that rail and some metro (Delhi and Kolkata) systems are shining examples of high-quality and high-capacity urban public transit, but buses were the original beast of this burden. Even as the baton is being handed over, bus services continue to carry a significant chunk of the ridership.
In the 2015-16 period, the Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC) recorded their highest yearly average in ridership—2.5 million commuters per day. Compare this to the city’s bus services, which recorded a massive 4.8 million ridership.
Most importantly, metro rail projects don’t come cheap. Chennai’s phase-I, which covers 45 km, pushed the city’s finances by about Rs 250 billion and the 108 km phase-II project is estimated to be a whopping Rs 850 billion—that is Rs 8 billion per kilometer!. The cost of the project is further borne by citizens, as the Chennai Metro is likely to be the costliest metro rail in the country. So the question arises, should a city spend Rs 8 billion on one kilometer of underground metro line and serve 10,000 passengers or build a 40 km high-quality bus rapid transit network which can serve upwards of a lakh passengers.
As sustainability becomes the need of the hour, bus-related transport systems are winning endorsements from cities and experts alike. According to the former Transportation Commissioner of New York City, Janette Sadik Khan, the model of roadway design—to move cars as fast as possible from point A to B—is outdated and needs to be updated. “Streets are the major capital asset for cities…They can be used to provide all sorts of mobility, like the Bus Rapid Transit system (BRTS). We can build high-capacity systems that can make it easier and more affordable and faster for people to move around,” said Khan in an interview to The Hindu.
So rather than neglecting this perennial lifeline, Indian cities need to take advantage of their already well-established bus systems. As Oscar Wilde put it, “Life is not complex. We are complex. Life is simple, and the simple thing is the right thing.” In the same context, urban mobility isn’t complex and a simple and humble transport medium such as the bus could unravel the complexities of Indian transportation.
Written by Rohit James
Edited by Kashmira Medhora Dubash














 India’s first car-free Sunday in Ahmedabad in 2012
India’s first car-free Sunday in Ahmedabad in 2012 People enjoying hop-scotch at the car-free Sunday in Coimbatore
People enjoying hop-scotch at the car-free Sunday in Coimbatore Father and daughter bonding over skipping at the car-free Sunday in Chenani
Father and daughter bonding over skipping at the car-free Sunday in Chenani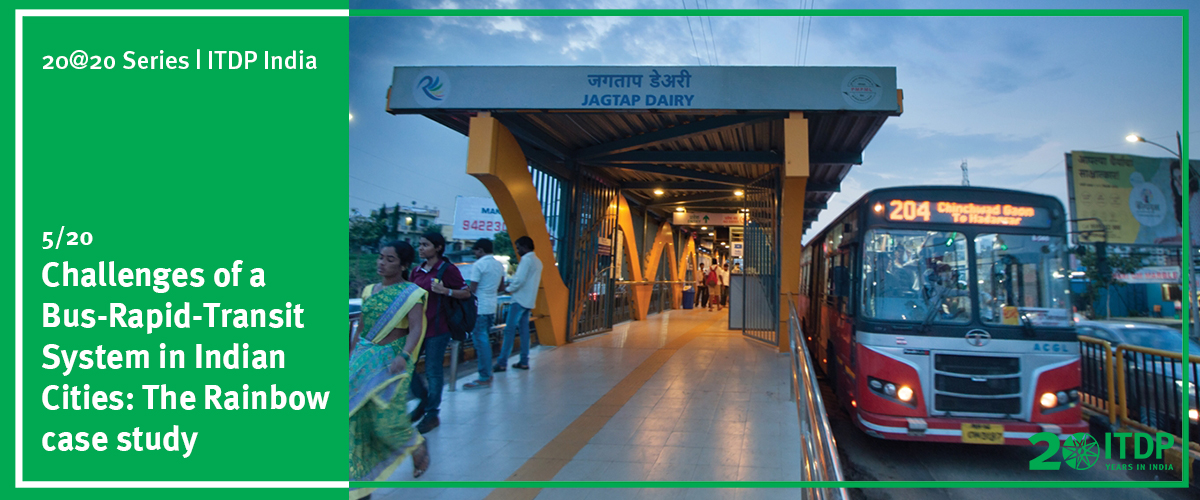













 The journey on the Janmarg is much quicker because the BRT enjoys centre-aligned, bus-only lanes
The journey on the Janmarg is much quicker because the BRT enjoys centre-aligned, bus-only lanes




























