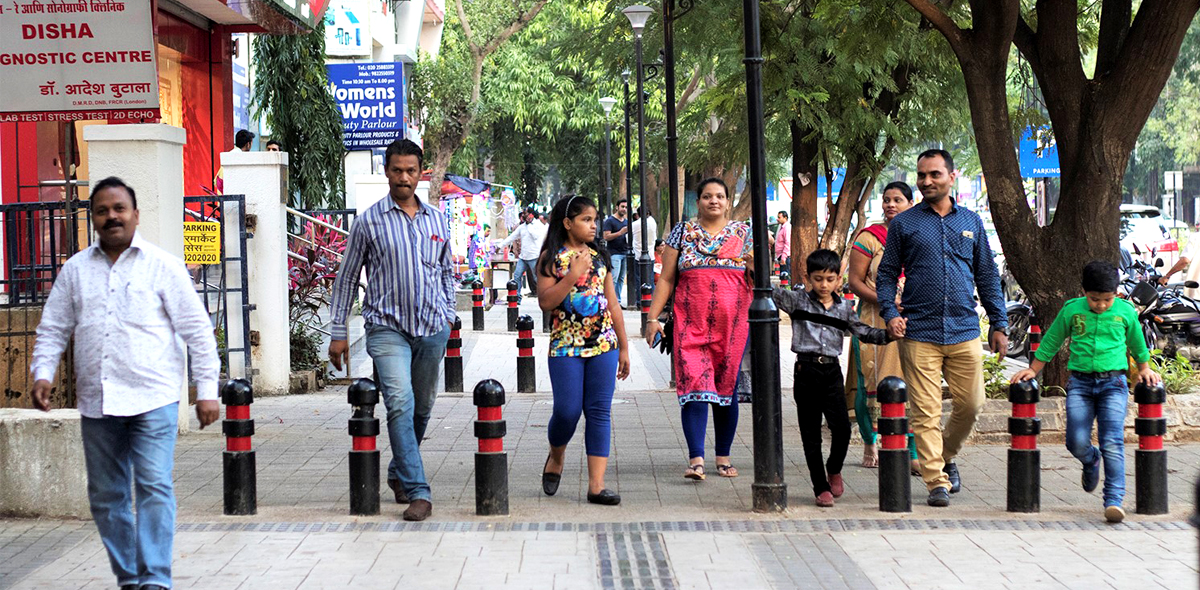
“I used to take my two-wheeler to travel the 3 kilometers between my house and the railway station. I’m now able to walk the stretch, thanks to the continuous footpath. Best part – I’ve lost 5 kilos and my diabetes!” Mr. Manimaran, a resident of Egmore in Chennai, is thrilled at the tremendous change that a safer and better footpath has brought about in his life.
The year 2017 witnessed many such impactful changes in the field of sustainable transportation all around the country, including cities which ITDP India Programme has been closely working with. Thanking all our supporters, we take a look at the year that passed by.

Pune broke ground on its ambitious Complete Streets networks – a 100km-network with its own financial resources and 45km through support from the National Smart Cities Mission. The first phase of these street design projects on JM Road and DP Road has already been lauded by the country, owing to the vibrancy of these redesigned streets. Pune’s Bicycle Plan, recently approved by the General Body, paves way for the creation of a 300km bicycle-track network in the city.
Having accomplished over 40km of Complete Streets, Chennai initiated the next phase of street design by inviting tenders in late October to redesign 22km of streets. The city tested out the design of 5 key intersections through a tactical urbanism approach – quick, temporary, on-ground interventions. Chennai also conducted another trial run of the proposed pedestrian plaza in Pondy Bazaar, the success of which fetched the project a sanction of of Rs 55 crores (~US $9 million) under the Smart Cities Mission.
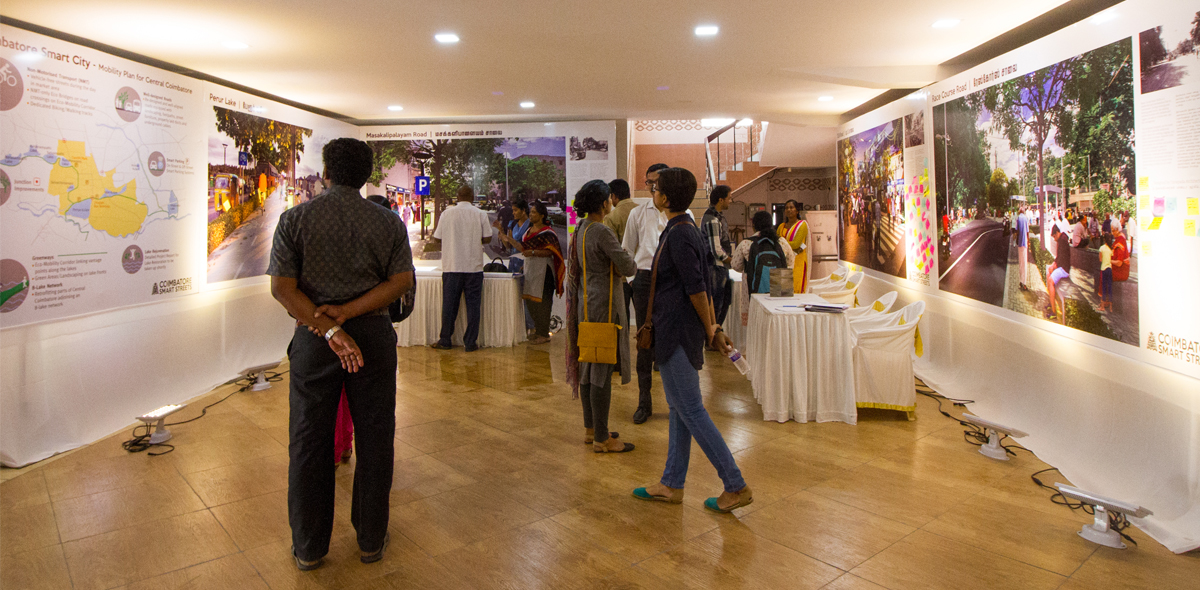
Smaller cities have also made remarkable progress this year in their Complete Streets programmes – Nashik appointed nationally-acclaimed urban designers to redesign its proposed street network of 50 kilometers, with 10 kilometers tendered out; and Coimbatore commenced construction of its Model Roads and hosted an interactive exhibition to inform the people of the design of the roads while collecting feedback. Coimbatore also started developing detailed implementation plans for its Greenways and Lake Restoration Project, which includes a 30km network of greenways (exclusive walking and cycling infrastructure) that crisscross the city and connect 8 water bodies.

Becoming one of the pioneering cities in parking management in the country, Ranchi implemented a progressive on-street parking management system on its busiest thoroughfare, Mahatma Gandhi Marg, with a twelve-fold increase in revenue. Inspired by the success of the pilot, the city has proposed to refine and expand the system to cover all key locations. The state of Jharkhand has also proposed to adopt a state-level parking policy.
Chennai recently invited tenders to select an operator for its proposed on-street parking management system covering 12000 equivalent car spaces on Bus Route Roads across the city. Since Pune is also working towards parking management, ITDP, in collaboration with GIZ-SUTP, facilitated and managed a two-day workshop on the topic, with international parking expert, Dr Paul Barter in the city. Participants included municipal officials, traffic police, public officials from other agencies as well as various local stakeholders.

An increase in demand for better public transport has provided the fillip to cities across the country to increase and improve their transit services. Chennai made considerable advancement in its BRT planning, with the interim report for Phase I approved by the state and a series of public consultation programmes organised to explain the significance of BRT to people and get their feedback on the various corridors.
In Pune, around 130 crore rupees was sanctioned to construct 13 new bus terminals to facilitate better integration of bus services with the proposed Metro Rail network. The city also commenced work on expanding the existing 38km Rainbow BRT by an additional 15km. Pune Mahanagar Parivahan Mahamandal Limited (PMPML) initiated the process of adding 200 feeder buses to its fleet, to improve connectivity between the city and the surrounding towns.
Public bicycle sharing (PBS) is emerging as a popular mode of public transit across the country. Pune piloted a dockless PBS system with 275 bicycles and signed an MoU with 4 vendors dealing with dockless systems. Two other cities are preparing for the installation of a PBS system – Ranchi and Chennai invited operators to submit proposals for setting up 1264 bicycles in 122 stations (Phase 1) and 5000 bicycles in 378 designated parking areas, respectively.

Successful and sustained on-ground changes invariably require the backing of well-framed guidelines, policies and financial plans – 2017 was marked by many of these. Two sets of guidelines – the Bus Rapid Transit (BRT) planning and design guidelines, and the Guidelines on Control and Regulation of Mixed Traffic in Urban Areas – prepared by ITDP, were approved by the apex committee of the Indian Roads Congress. These guidelines will apply for all cities across India and guide them towards low-carbon mobility.
The Government of Jharkhand adopted an inclusive TOD policy that focuses on equitable development of cities in the state, so that a majority of the population lives and works in areas with safe and accessible walking and cycling facilities integrated with reliable and high-quality public transport.
The Government of Maharashtra published a draft of the State Urban Transport Policy, which promotes low-carbon & equitable mobility and urban development by prioritising public transport (PT) and non-motorised transport (NMT). Furthermore, over half of Pune’s total transportation budget of 1100 crore rupees was allocated towards sustainable transport development for the financial year 2017-18. In the South, Coimbatore adopted a Street Design and Management Policy that focuses on creating equitable and sustainable mobility options and expanding their use.

The realisation that sustainable urban development will remain elusive without integrating women’s safety and comfort in urban transport, has generated momentum to include gender as a key factor in transport planning. Bringing this subject to the fore and as a first of its kind, a paper on Women and Transport in Indian Cities was created by ITDP and Safetipin, and released at a national workshop on gender and transit conducted by the two organisations. This paper identifies indicators, service level benchmarks and processes for integrating a gender perspective in urban transport projects, policies and programs along with good practice case studies.
2017 was a year of radical planning indeed, with many grand plans conceived, developed and initiated for sustainable transportation. With all these plans set to materialize in the coming months, 2018 will be a year of implementation and tangible transformation. Looking forward to a great year ahead: Happy New Year!