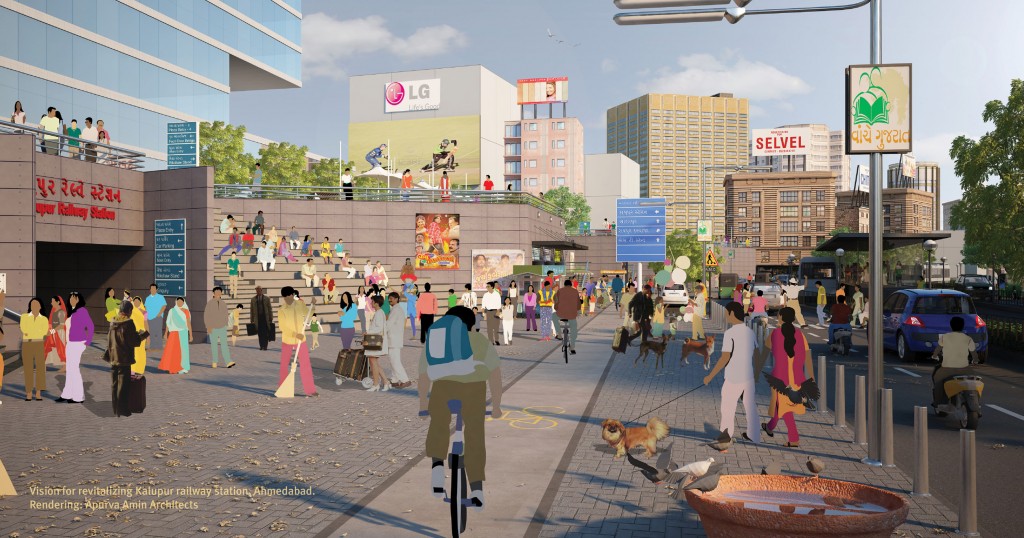
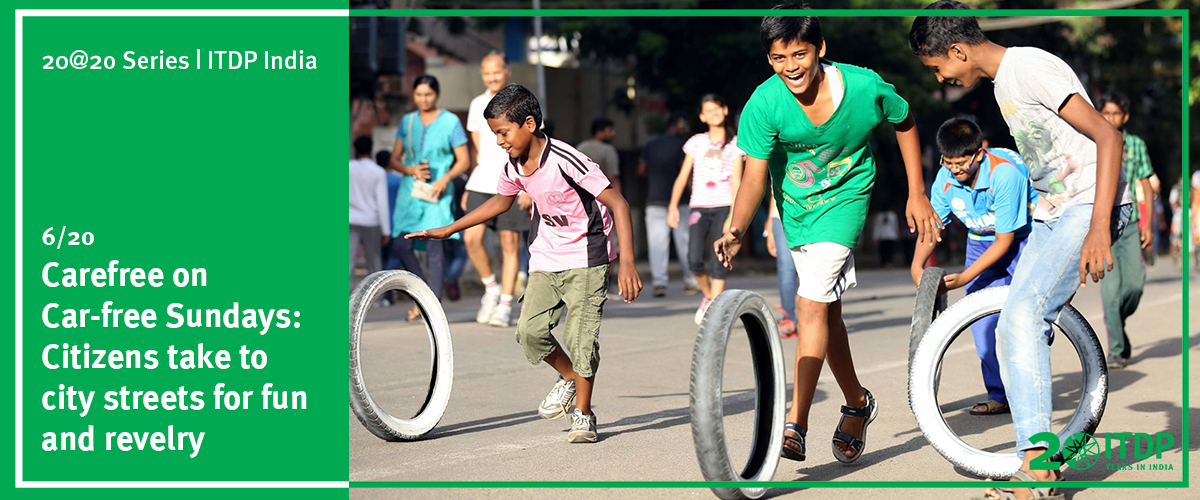Imagine an arterial road in your city. Now, place a child running about in that stretch. Fair to assume that your brows twitched at the thought of these two events aligning. Though stark, urban dwellers are naturalised to the danger that arterial roads or streets in general hold. But to hold a static entity accountable is unfair. So where does the buck stop?
Let’s reimagine this sequence of events. Same arterial city road and same child running about carefree. This time though, cordon off vehicles from the section. Suddenly, the road seems to be devoid of chaos. It even becomes an oasis where people can come together to run, play, and enjoy themselves to their heart’s content.
Isn’t it bewildering how one component can drive our stress up the walls and still be considered an integral part of our lives. This is exactly what the “Car-free” initiative was conceptualised to debunk. Originated in the Netherlands and Belgium during the 1956 Suez Crisis, the move was planned to ration petroleum. But it took its true form in 1958, when New York City residents blocked vehicles into their neighbourhood to protest the extension of a road at the cost of a public space.
As vehicles started taking over our streets and lives, the initiative gained prominence to counter this menace. And it is with the same intention that the initiative made its way into the Indian quarters. The “Car-free Sundays” drive, proposed by ITDP India Programme in collaboration with Riverside School and other partners, was first introduced to Ahmedabad in 2009. Every Sunday, citizens were given unconditional access to three arterial stretches to experience the freedom of walking and cycling on safer car-free streets.
 India’s first car-free Sunday in Ahmedabad in 2012
India’s first car-free Sunday in Ahmedabad in 2012
It wasn’t long before other states recognised the transformative nature of the initiative. Tamil Nadu and Maharashtra were quick to come on board and transform their streets into vibrant spaces for citizens, not vehicles, to occupy.
Leading the charge in Tamil Nadu was Coimbatore. The dialogue, facilitated by ITDP, was a success. All partners –including the Coimbatore City Municipal Corporation, Residents Awareness Association of Coimbatore (RAAC), print media partners and the residents– realised that the concept would help improve walking and cycling conditions in the city.
The Corporation and the Coimbatore Police left no stones unturned to help citizens reclaim landscape lost to vehicles. With prior public consultation workshops for residents, the campaign was launched across two stretches –DB Road and T V Swamy Road– for a total of 1.7km, in 2015. This sense of emancipation was refreshing, as many came in droves to be part of the revelry. Soon accolades started pouring in, with the campaign being honoured with the Best Project Award, Non-Motorised Transport category, by India’s National Ministry of Urban Development.
 People enjoying hop-scotch at the car-free Sunday in Coimbatore
People enjoying hop-scotch at the car-free Sunday in Coimbatore
The obvious impact was soon realised by Chennai and it didn’t take much for city officials and the police to join the bandwagon, with ITDP again playing a hand holding role in collaboration with Chennai City Connect and The Hindu (media partners). Titled “Namma Chennai Namakke” (Our Chennai for Ourselves), many residents took an instant liking to the idea.
“I would love to see children aimlessly ride their cycles on the road…or adults playing badminton and pet enthusiast take their companions for a walk. I personally would indulge my pet, without the fear of him/her getting hit by a car,” said Jennifer Jacob-Murali, resident of Chennai.
 Father and daughter bonding over skipping at the car-free Sunday in Chenani
Father and daughter bonding over skipping at the car-free Sunday in Chenani
Every Sunday, the ruckus of vehicles were replaced by that of laughter and excitement. Of kids being kids and parents joining the act. Of people dancing, doing yoga, and enjoying art and craft. Of citizens, young and old, not surrendering their right to walk, run, and cycle to the chagrin of fuel guzzling automobiles.
Today, these cities have taken a step ahead towards sustainable urban transport solutions with Chennai adopting a Non-Motorised Transport Policy and Coimbatore adopting the Street Design and Management Policy. Car-free Sundays helped citizen to wake up to the possibility of enjoying public spaces like roads and streets without the hindrance and dread of vehicles. Its success gave momentum to the ‘Model Roads’ project, as citizens demanded better walking and cycling infrastructure across Coimbatore.
Not even John Lennon could have imagined how vehicles would take over lives, leaving us struggling to find our way. So an ode to his legendary vision, with a twist of our own.
Imagine there are no vehicles
It’s easy if you try
No fumes around us
Only people and the sky
Imagine all the people living for today
Cover image courtesy: Times of India, Coimbatore.