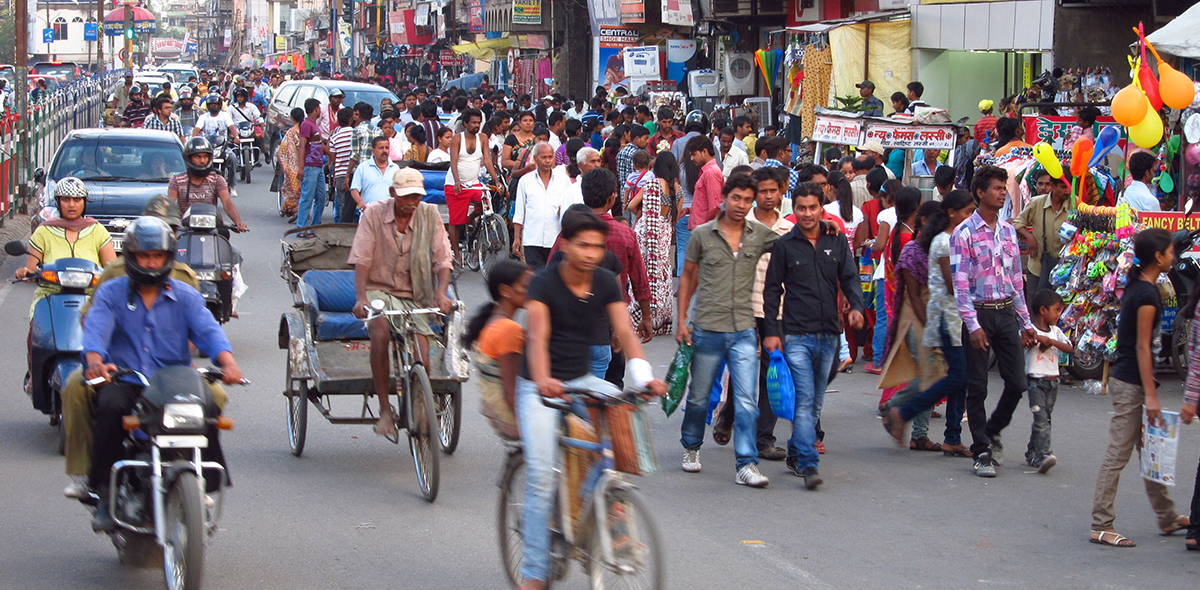
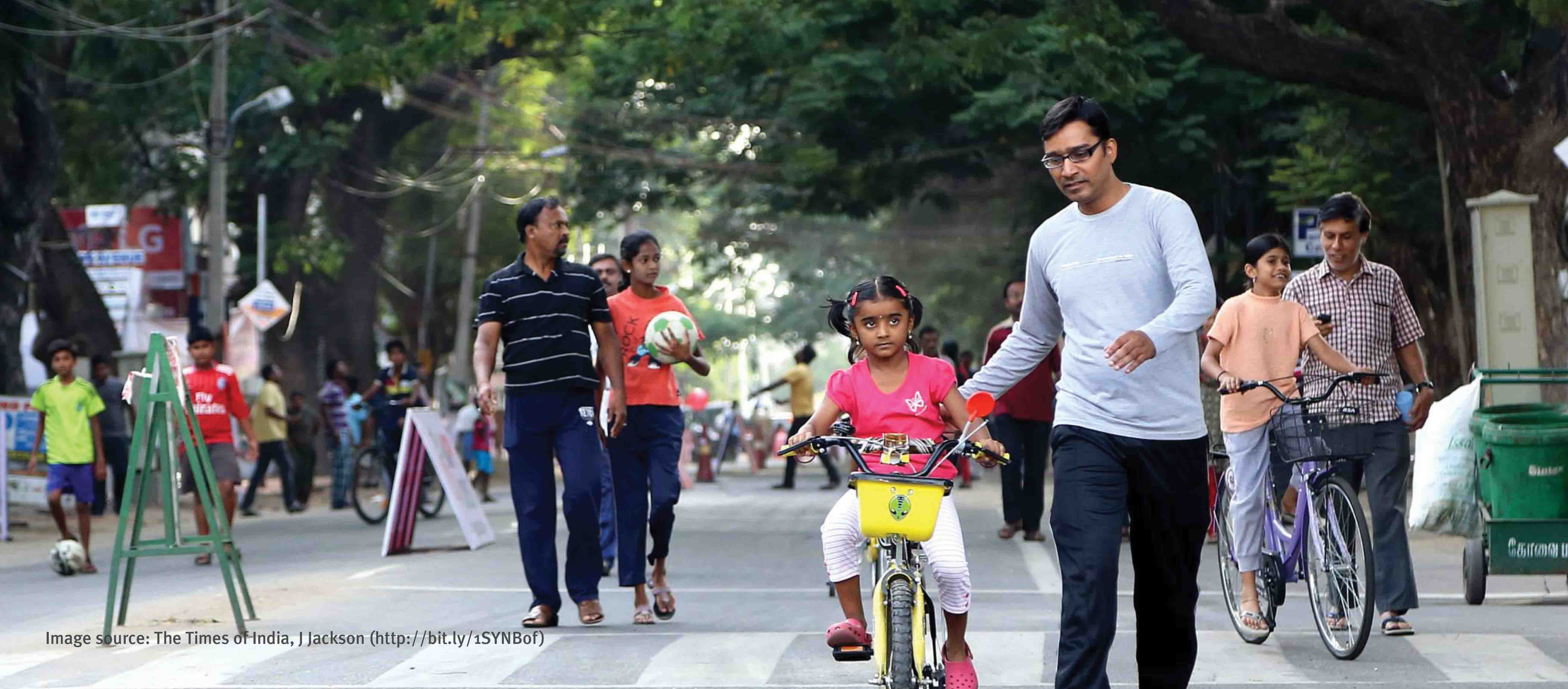One of India’s fastest growing business and IT hubs, Pune has been constantly planning and executing sustainable initiatives even before India envisaged the Smart City Mission. For many Indian cities, the national initiative is its first step towards sustainability. However, for Pune, the mission acted as a catalyst. It significantly boosted confidence of the city administration, who not only fast tracked implementation of existing projects, but also expanded their scope and added many new projects to the city’s kitty. The city is making rapid progress in expanding its bus rapid transit (BRT) network, strengthening its public transportation system and implementing projects to make its streets pedestrian and cyclist friendly.
On account of its successes, late June 2016, Pune was selected as the destination for the first anniversary celebrations of India’s smart city mission. The Prime Minister Narendra Modi, who graced the occasion, launched 84 projects across 20 smart cities. Of these projects, 14 were from Pune. The new projects will give the city the required thrust to make IT based improvements in its public transport system.
Pune’s high quality mass transit system—Rainbow BRT, launched in September 2015—is witnessing constant expansion. The city is exploring ways to converge different funding sources and further strengthen the system. While a new 8 km corridor is planned under Smart City’s area based development in Aundh-Baner-Balewadi region (ABB), the city’s progressive 2016-17 budget has allocated funding for two more corridors, which will expand the Rainbow network by 15 km. In addition, the “pilot” BRT corridors will be redesigned with “Rainbow” style median stations to provide level boarding.

A Rainbow BRT bus enters a station equipped with safe access ramps that allows everybody, especially the elderly and the differently able, to use the system.
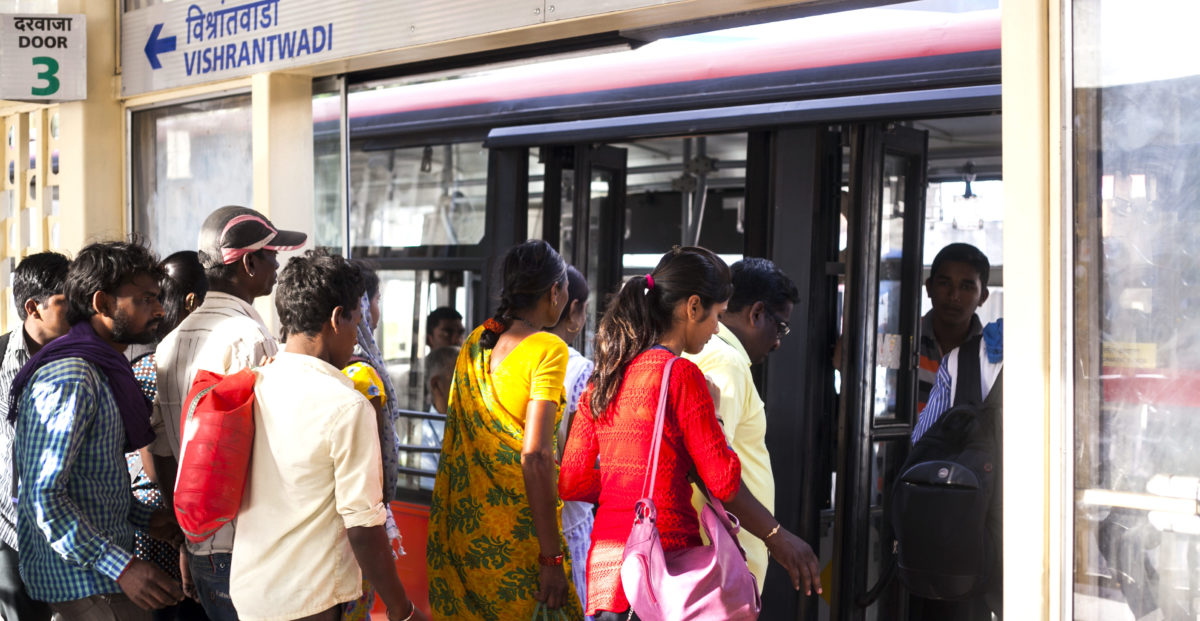
Similarly, the city bus service is also undergoing a massive transformation. The city is investing heavily on expanding its fleet size—by almost doubling the operational fleet. Pune’s existing bus fleet of about 2,055 buses will be augmented with an addition of 1550 buses by 2017—to achieve 25% of total trips by public transport. As part of the Smart City Mission, Pune will improve bus services through ITMS and real-time tracking of all its buses. A central control centre will monitor driving quality of buses and services at all levels. The city has also embarked on developing websites, mobile apps, and passenger information systems to give commuters critical information on expected time of arrival of buses and schedules. A common mobility card—‘Mobility Integration (MI)’—has been launched to enable cash-free payments on public transport systems.
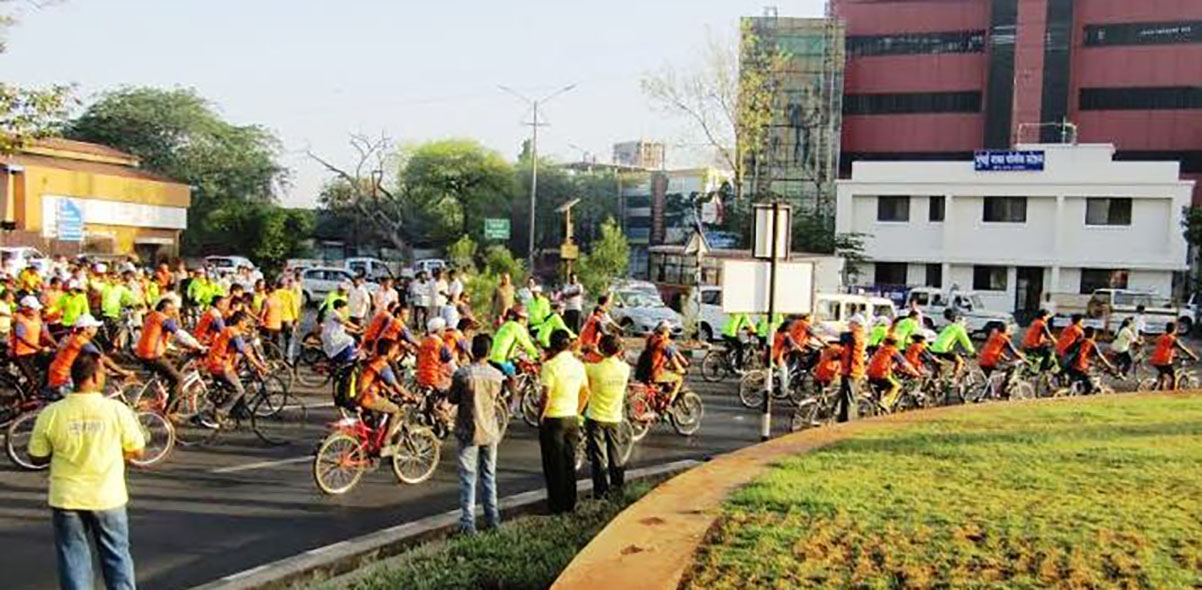
The city is also looking towards improving conditions for its pedestrians and cyclists. Most arterial roads in the city will be redesigned as ‘Complete Streets’—including 45 km of streets in the ABB region under the smart city proposal and 100 km of streets across the city through PMC budget. To re-establish its cycling culture, Pune is developing a cycle plan for the city, with an objective of increasing the cycling modal share from today’s 9% to 25% by 2031. A bicycle sharing system is also proposed in the ABB region. To ensure that quality remains consistent during the planning, designing and implementation of its non-motorised transport initiatives, the city is setting up a street design cell, as well as adopting a pedestrian policy and urban street design guidelines.
Pune’s commitment to improving mobility is placing the city as a leader in India, on sustainable transport and development. By embracing the direction set by the national mission and expanding its scope across the city using both national and city funding, Pune is setting a benchmark for all other cities in the Indian urban panorama.
Cover picture source: www.punesmartcity.in