Pune, Coimbatore and Chennai have been making huge progress creating sustainable cities. Each has made great strides in recent years, laying the groundwork for even bigger changes to come. Thanks to their demonstrated commitment to act, in addition to well-developed plans for next steps, all three have been selected for the first round of India’s national Smart Cities Mission.
Right now, experts predict that about 25-30 people are migrating every minute to major Indian cities from rural areas in search of better livelihood and better lifestyles. It is estimated that by 2050, Indian cities will house nearly 843 million people. This massive increase in population will put incredible pressure on India’s cities, requiring new infrastructure for transportation, energy, and safety. To address these imminent issues, the Government of India has allocated Rs 48,000 crore to create the Smart Cities Mission, a programme dedicated to helping cities invest in sustainable infrastructure and growth.
As part of the Smart Cities Mission, these three selected cities (see the full list here) have each proposed to invest over 600 Crore rupees in sustainable transport projects. By pegging this money to tangible, area-based improvements, these cities have a clear plan to transform over the next 5 years, bringing widespread socio-economic benefits to a large section of society. ITDP is proud to have partnered with Pune, Coimbatore, and Chennai to chart out their sustainable paths for the future.
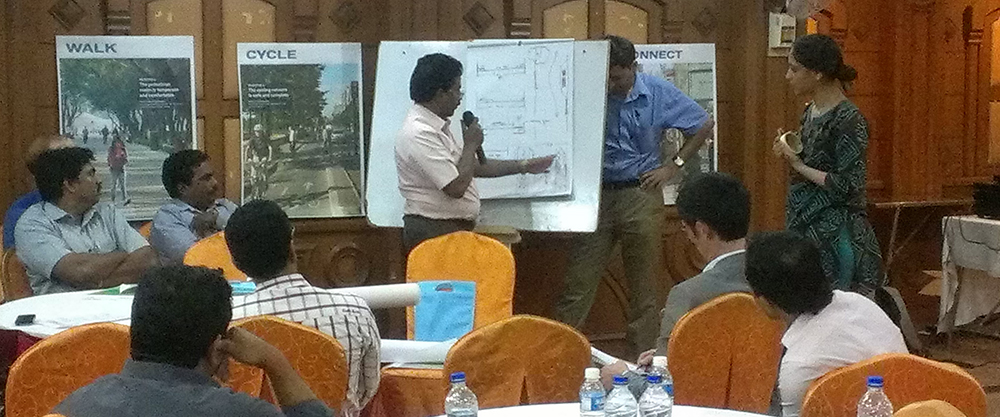
ITDP has been working with these cities in different roles, providing technical support to projects, capacity building for officials, and creating community engagement at various levels. In the twin cities of Pune and Pimpri-Chinchwad, ITDP helped implement the Rainbow BRT, incorporating best practices in BRT planning and design. ITDP has been instrumental in helping Chennai adopt a Non-Motorized Transport Policy and overseeing its implementation through street design and engaging with citizens through initiatives like car-free Sundays. In Coimbatore, the Namma Kovai Namakke (Our Coimbatore Ourselves) campaign, initiated by ITDP, sparked citizen demand for better pedestrian facilities, all of which formed the groundwork for the Smart City proposals developed by these cities.
In the next 5 years, Pune aims to increase the mode share of public transport from 18 percent to 50 percent by augmenting its bus fleet and improving bus services using Intelligent Traffic Management Systems (ITMS). The city also aims to expand its high quality BRT network by 30 km and improve access to transit by creating 75 km network of footpaths and cycle tracks.

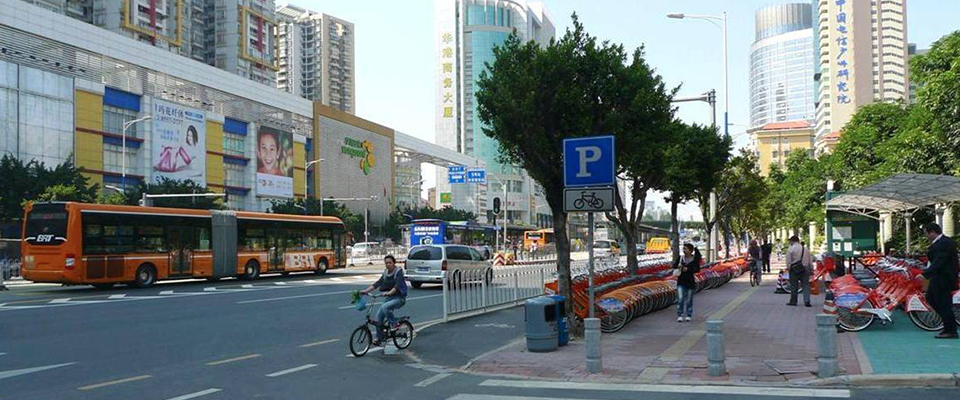
To facilitate easy interchange between Rainbow BRT and other buses, a transit hub is proposed at Anudh Baner Balewadi, Pune, along the lines of the Kiwale terminal pictured above.
In keeping with its NMT policy, Chennai aims to develop ‘Complete Streets’ and build footpaths to cover 80% of its major roads. A city-wide cycle sharing system with 3000 cycles and an IT-based parking management system are also expected to give a major thrust to walking and cycling while restricting private vehicle use.

Better NMT facilities are proposed in T. Nagar, a commercial and retail hub of Chennai.
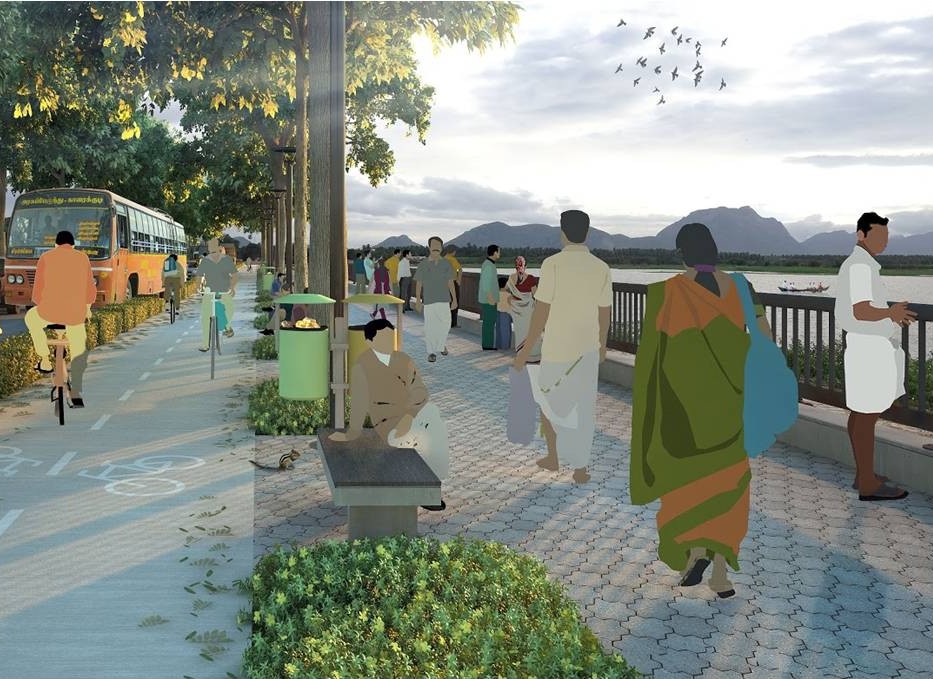
Non-motorised transport is a key focus for Coimbatore as well, where the city aims to create NMT infrastructure along 75 percent of its primary and secondary road networks before 2020. A 30 km network of greenways connecting major lakes in the city is expected to improve quality of open space for its residents. The city also aims to increase mode share of public transport from 42 percent to 60 percent by modernising and expanding public bus services.
Congratulations to these cities, and all the selected Smart Cities, for the exciting work preparing India’s cities for a more sustainable, brighter future.